| Inhibition of chemoresistance and enhancement of chemosensitivity |
|

|

|
Page 2 of 2
RP-BVDU co-treatment inhibits chemoresistance and enhances chemosensitivity
Overexpression of specific genes can render cells
resistant to apoptosis (programmed cell death), thereby favoring
malignant growth. Moreover, since most chemotherapeutic agents kill
tumour cells by inducing apoptosis, overexpression of such genes can
lead to a multidrug resistance phenotype. Beyond that, gene
amplification and recombination (new combination of genes), of many
chromosomal regions is the cause of altered gene expression in a
variety of human tumours. The amplification and overexpression of the
amplified target genes produces a selective advantage for tumour cells,
thereby playing an important role in the pathogenesis and prognosis of
cancer disease. Often tumour cells that are resistant to chemotherapy
have been affected by the amplification of a small group of genes which
are responsible for this resistance. For this reason, an obstruction of
the gene amplification process during the progression phase could lead
to an improvement in chemotherapy.
Resistant tumours often share a similar characteristic, i.e. some of their genes have multiplied (amplified) themselves. These are mostly oncogens (cancer producing genes) or genes which pass on resistance against several cytostatic agents (multidrug resistance genes = MDR). These MDR genes produce a protein (P-glycoprotein) which removes foreign or cytostatic substances from the cell. If the MDR genes reproduce themselves, then they will produce a similar increased amount of Pglycoprotein. Consequently, the drugs are driven out of the cancer cells, thereby losing their effectiveness. The tumour can thus grow uncontrolled. Since it has been discovered that the first steps of gene amplification are based on a recombination mechanism, research has been concentrating on developing anti-recombinogenic substances which are active in dosages applicable to humans. The antirecombinogenic substance RP-BVDU meets both requirements. It inhibits the induction of gene amplification mediated multi-drug resistance (MDR) by adriamycin in tumour cells.
Clinical pilot study 2. Infectious diseasesTwo main factors can influence whether bacteria will become insensitive to an antibiotic: the prevalence of resistance genes which give rise to proteins that shield bacteria from an antibiotic's effects, and the extent of antibiotic use. When an antibiotic attacks a group of bacteria, individuals that are highly susceptible to the antibiotic will die. But bacteria that have some resistance from the start, or that acquire it later through mutation or gene exchange by recombination, may survive. Those cells, facing reduced competition from susceptible bacteria, will then go on to proliferate. When confronted with an antibiotic, the most resistant cells in a group will inevitably outcompete all others.
RP-BVDU co-treatment inhibits chemoresistance and enhances chemosensitivity
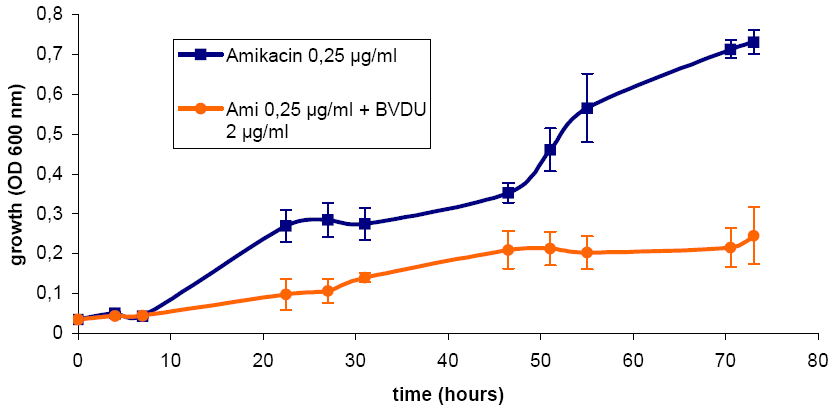
Fig. 1: Inhibition of Amikacin resistance of E. coli J53 (RP4) by co-treatment with RP-BVDU (3-4 parallel cultures each).
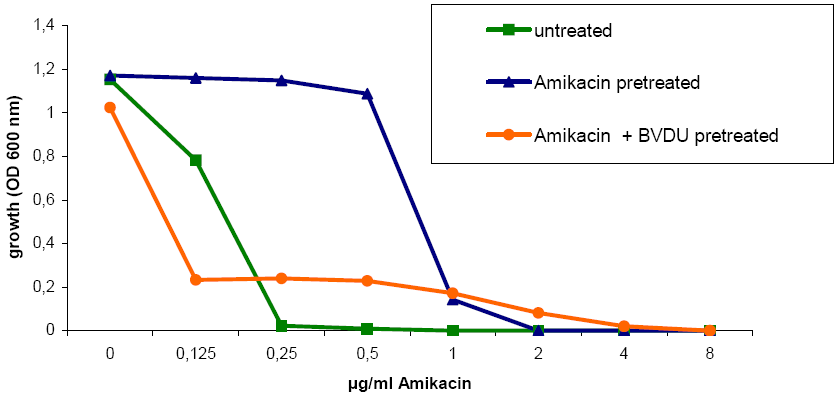
Fig. 2: Minimal growth inhibition concentration of Amikacin for different pretreated E. coli J53-strains. Contact:
RESprotect GmbH
Prof. Dr. Rudolf Fahrig Fiedlerstr. 34 01307 Dresden, Germany phone: +49 351 4503200
|
||||