| Inhibition of Induced Chemoresistance by Cotreatment with BVDU |
|

|

|
Page 7 of 12
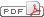
Fig. 3. Effect of BVDU combinatorial treatment on protein expression. A, Western blot analysis, expression of STAT3, JUN-D, and caspase-3 (proteolytically activated form) in response to cytostatic drug treatment. The expression levels were determined densitometrically (r. = recovery, see Fig. 1C). B, NQO1 enzyme activity (mean value ± SD, six independent experiments).
We investigated NQO1 activity in cell extracts (16)
after treatment with the cytostatic drugs ± BVDU (Fig. 3B). BVDU cotreated cells showed higher NQO1 activity than untreated control cells or cells treated with cytostatic drugs only. Interestingly, cells treated with MMC+BVDU, which caused the strongest antiproliferative effect, did not enhance NQO1 activity.
To elucidate the effects of BVDU, we performed a two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and identified differentially expressed proteins by MALDI-MS (Table 1). During combinatorial MMC+BVDU treatment, or during recovery (MMC omitted, BVDU present) from combinatorial treatment, the expression of three major "clusters" of protein classes was affected: (a) microfilamental (or regulatory) proteins were up-regulated during recovery (actins, tubulin, myosin, and tropo-modulin); (b) proteins involved in ATP generation were down-regulated (succinate dehydrogenase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and malic enzyme; however, malate dehydrogenase was up-regulated); and (c) proteins regulating DNA repair were suppressed (APEX and UBE2N). One protein with oncogenic potential, DDX1, was affected by BVDU alone. In total,
Table 1 Effects of cotreatment of MMC with BVDU on protein expression
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



 75% of the spots were identified by MALDI-MS.
75% of the spots were identified by MALDI-MS.
 subunit; PAFAH1B1
subunit; PAFAH1B1